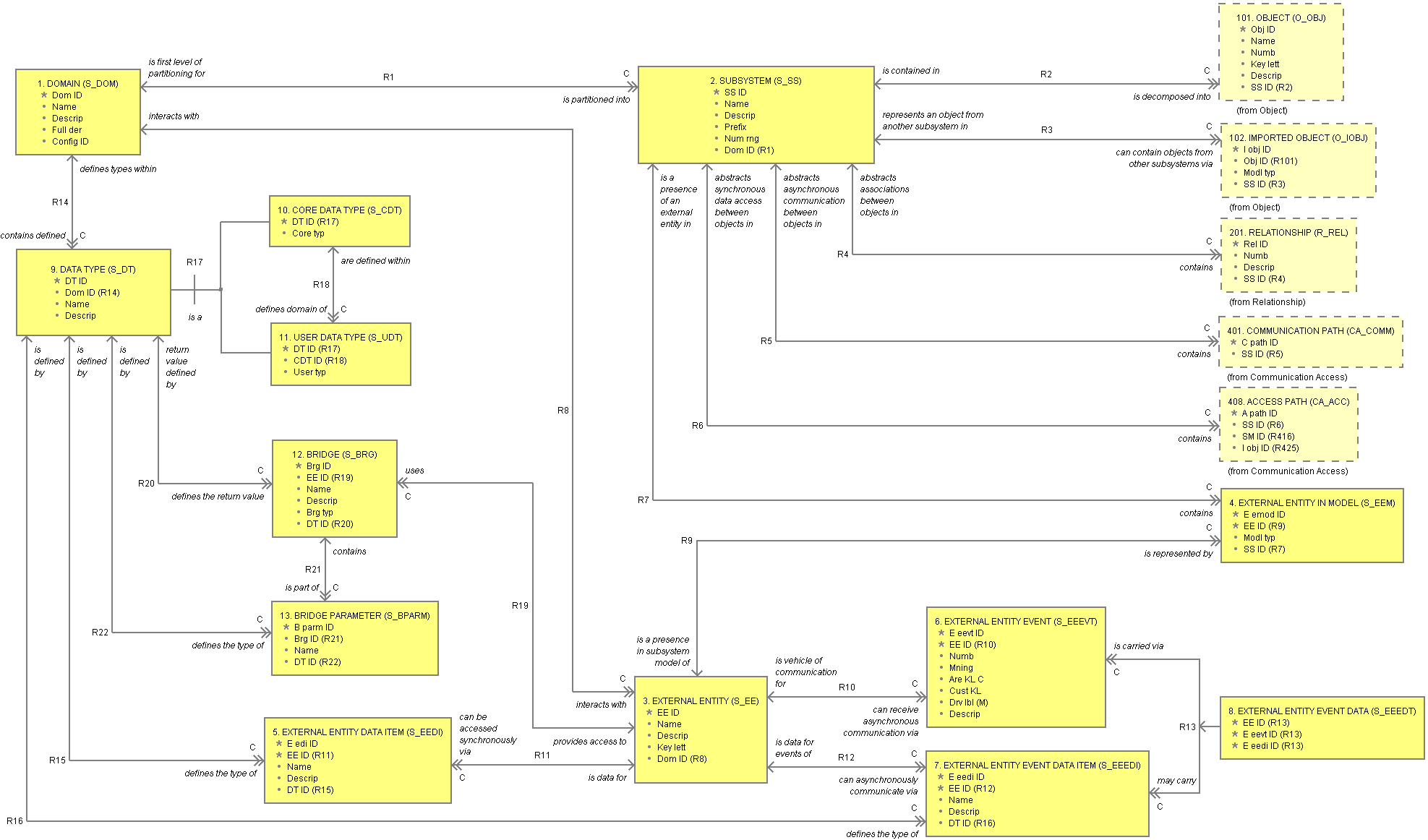
A Subsystem is based on the partitioning of an entire Domain. The number of Subsystems in a Domain is dependent upon the Domain subject matter and complexity.
A Subsystem is composed of objects that tend to cluster, i.e., they have many interconnections with one another but few interconnections with objects in different clusters.
Inter-Subsystem relationships, communications, and accesses are captured in the Subsystem Relationship Model (SRM), Subsystem Communication Model (SCM), and Subsystem Access Model (SAM) respectively.

|
Identifiers: A typical software system generally consists of distinct and independant subject matters. A Shlaer/Mellor analysis partition is based within each of these subject matters - each subject matter is called a Domain. A Domain is inhabited by its own conceptual entities (called objects). A domain may be partitioned into subsystems depending upon it's complexity. Each Domain is given a mission statement which provides a charter for the construction of the OOA models. 1.1. Domain.Dom_IDFull Name: Domain Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 1.2. Domain.NameFull Name: Domain Name Data Type: string 1.3. Domain.DescripFull Name: Domain Description Data Type: string 1.4. Domain.Full_DerFull Name: Fully Derived Flag A flag indicating whether the Object Communication Model and Object Access Model are fully derived from the information contained in the Object Information Model and Action Specifications. Domain: Data Type: boolean 1.5. Domain.Config_IDFull Name: Configuration Identifier The configuration ID of the version mangement configuration which the domain is a part of (See Page 57 of BridgePoint Tool Guide). This ID can be used to access the V_CONFIG record corresponding to the Domain/Subsystem Configuration. Data Type: arbitrary_id |
|
Identifiers: A Subsystem is based on the partitioning of an entire Domain. The number of Subsystems in a Domain is dependent upon the Domain subject matter and complexity. A Subsystem is composed of objects which tend to cluster, i.e., objects which have many relationships with one another but few relationships with objects in different clusters. Inter-Subsystem relationships, asynchronous communications, and synchronous accesses are captured in the Subsystem Relationship Model, Subsystem Communication Model and Subsystem Access Model, respectively. 2.1. Subsystem.SS_IDFull Name: Subsystem Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 2.2. Subsystem.NameFull Name: Subsystem Name Data Type: string 2.3. Subsystem.DescripFull Name: Subsystem Description Data Type: string 2.4. Subsystem.PrefixFull Name: Subsystem Keyletter Prefix The subsystem keyletter prefix is used when objects are created in the subsystem - the subsystem keyletter prefix is used as the default prefix in the object keyletters. Data Type: string 2.5. Subsystem.Num_RngFull Name: Subsystem Number Range Start The subsystem number range start is used when objects and relationships are created in the subsystem - the subsystem number range start is used as the default auto-numbering start value in the newly created Object's number and newly created Relationship's number. Data Type: integer 2.6. Subsystem.Dom_ID (R)Domain: Same as Domain.Dom_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: An External Entity represents something outside of the Domain being modeled that interacts with objects within the Domain being modeled. The interactions are showed by Event Communications in the Object Communication Models and Data Accesses in the Object Access Models. Each External Entity is given a unique name and keyletters within a Domain. 3.1. External Entity.EE_IDFull Name: External Entity Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 3.2. External Entity.NameFull Name: External Entity Name Data Type: string 3.3. External Entity.DescripFull Name: External Entity Description Data Type: string 3.4. External Entity.Key_LettFull Name: External Entity Key Letters Data Type: string 3.5. External Entity.Dom_ID (R)Domain: Same as Domain.Dom_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: The External Entity in Model is the presence of an External Entity in a model such as the Object Communication Model or Object Access Model. The same External Entity can be represented by more than one External Entity in Model in the same model to enhance model layout. 4.1. External Entity in Model.EEmod_IDFull Name: External Entity in Model Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 4.2. External Entity in Model.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
4.3. External Entity in Model.Modl_TypFull Name: Model Type Domain: Value indicates what type of model the External Entity is in:
Data Type: integer 4.4. External Entity in Model.SS_ID (R)Domain: Same as Subsystem.SS_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: Interactions between Objects and External Entities shown in the Object Access Models involve the access of data. An External Entity Data Item is a characteristic of an External Entity that an Object may read. 5.1. External Entity Data Item.EEdi_IDFull Name: External Entity Data Item Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 5.2. External Entity Data Item.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
5.3. External Entity Data Item.NameFull Name: External Entity Data Item Name Data Type: string 5.4. External Entity Data Item.DescripFull Name: External Entity Data Item Description Data Type: string 5.5. External Entity Data Item.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: An External Entity Event identifies an interaction between an Object and an External Entity and is captured on an Object Communication Model. Each External Entity Event is given a unique label. 6.1. External Entity Event.EEevt_IDFull Name: External Entity Event Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 6.2. External Entity Event.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
6.3. External Entity Event.NumbFull Name: External Entity Event Number Data Type: integer 6.4. External Entity Event.MningFull Name: External Entity Event Meaning Data Type: string 6.5. External Entity Event.Are_KL_CFull Name: Are Key Letters Custom Flag This is a flag that indicates whether custom label keyletters are used for the External Entity Event. Domain: Data Type: boolean 6.6. External Entity Event.Cust_KLFull Name: External Entity Event Label Key Letters Data Type: string 6.7. External Entity Event.Drv_Lbl (M)Full Name: Derived External Entity Event Label Holds the event label - derived by concatenating the key letters and the event number.
If the
If the Data Type: string 6.8. External Entity Event.DescripFull Name: External Entity Event Description Data Type: string |
|
Identifiers: Synchronous interactions from Objects to External Entities modeled by allowing an Object to synchronously access the data items of the External Entity - the interaction is captured on the Object Communication Model. An External Entity Data Item is a characteristic of an External Entity. 7.1. External Entity Event Data Item.EEedi_IDFull Name: External Entity Event Data Item Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 7.2. External Entity Event Data Item.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
7.3. External Entity Event Data Item.NameFull Name: External Entity Event Data Item Name Data Type: string 7.4. External Entity Event Data Item.DescripFull Name: External Entity Event Data Item Description Data Type: string 7.5. External Entity Event Data Item.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: This object serves as a correlation table. 8.1. External Entity Event Data.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
8.2. External Entity Event Data.EEevt_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity Event.EEevt_ID References:
8.3. External Entity Event Data.EEedi_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity Event Data Item.EEedi_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: An analyst can assign a data type to the various data items in the OOA, e.g., object attribute, state model event data item, transformer/bridge parameter/return value. This data type does not capture the representation of the data items, but rather, the characteristics of the data items including:
9.1. Data Type.DT_IDFull Name: Data Type Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 9.2. Data Type.Dom_ID (R)Domain: Same as Domain.Dom_ID References:
9.3. Data Type.NameFull Name: Data Type Name Data Type: arbitrary_id 9.4. Data Type.DescripFull Name: Data Type Description Data Type: string |
|
Identifiers: Core Data Types are those data types which are fundamental, or core, to all data types. 10.1. Core Data Type.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
10.2. Core Data Type.Core_TypFull Name: Core Data Type Core Type Domain: Valid Core Types:
Data Type: integer |
|
Identifiers: User Data Types are those data types which have been derived from the core data types - they typically are derived because more assumptions can be made about the range of values which can be stored or they are derived to serve as a common funneling point for several data items which share some common data type. 11.1. User Data Type.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
11.2. User Data Type.CDT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
11.3. User Data Type.User_TypFull Name: User Data Type User Type Domain: Data Type: integer |
|
Identifiers: A Bridge is a method associated with an External Entity - bridges can be synchronously called from Action Specifications. 12.1. Bridge.Brg_IDFull Name: Bridge Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 12.2. Bridge.EE_ID (R)Domain: Same as External Entity.EE_ID References:
12.3. Bridge.NameFull Name: Bridge Name Data Type: string 12.4. Bridge.DescripFull Name: Bridge Description Data Type: string 12.5. Bridge.Brg_TypFull Name: Bridge Type Domain: Data Type: integer 12.6. Bridge.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
|
|
Identifiers: A parameter to a bridge. 13.1. Bridge Parameter.BParm_IDFull Name: Bridge Parameter Identifier Data Type: arbitrary_id 13.2. Bridge Parameter.Brg_ID (R)Domain: Same as Bridge.Brg_ID References:
13.3. Bridge Parameter.NameFull Name: Bridge Parameter Name Data Type: string 13.4. Bridge Parameter.DT_ID (R)Domain: Same as Data Type.DT_ID References:
|
| R1. | Domain IS PARTITIONED INTO Subsystem (1:Mc) |
| Subsystem IS FIRST LEVEL OF PARTITIONING FOR Domain |
Formalization:
| Subsystem.Dom_ID | → | Domain.Dom_ID |
| R2. | Subsystem IS DECOMPOSED INTO Object (1:Mc) |
| Object IS CONTAINED IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| Object.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R3. | Subsystem CAN CONTAIN OBJECTS FROM OTHER SUBSYSTEMS VIA Imported Object (1:Mc) |
| Imported Object REPRESENTS AN OBJECT FROM ANOTHER SUBSYSTEM IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| Imported Object.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R4. | Subsystem CONTAINS Relationship (1:Mc) |
| Relationship ABSTRACTS ASSOCIATIONS BETWEEN OBJECTS IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| Relationship.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R5. | Subsystem CONTAINS Communication Path (1:Mc) |
| Communication Path ABSTRACTS ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATION BETWEEN OBJECTS IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| Communication Path.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R6. | Subsystem CONTAINS Access Path (1:Mc) |
| Access Path ABSTRACTS SYNCHRONOUS DATA ACCESS BETWEEN OBJECTS IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| Access Path.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R7. | Subsystem CONTAINS External Entity in Model (1:Mc) |
| External Entity in Model IS A PRESENCE OF AN EXTERNAL ENTITY IN Subsystem |
Formalization:
| External Entity in Model.SS_ID | → | Subsystem.SS_ID |
| R8. | Domain INTERACTS WITH External Entity (1:Mc) |
| External Entity INTERACTS WITH Domain |
Formalization:
| External Entity.Dom_ID | → | Domain.Dom_ID |
| R9. | External Entity IS REPRESENTED BY External Entity in Model (1:Mc) |
| External Entity in Model IS A PRESENCE IN SUBSYSTEM MODEL OF External Entity |
Formalization:
| External Entity in Model.EE_ID | → | External Entity.EE_ID |
| R10. | External Entity CAN RECEIVE ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATION VIA External Entity Event (1:Mc) |
| External Entity Event IS VEHICLE OF COMMUNICATION FOR External Entity |
Formalization:
| External Entity Event.EE_ID | → | External Entity.EE_ID |
| R11. | External Entity Data Item IS DATA FOR External Entity (Mc:1) |
| External Entity CAN BE ACCESSED SYNCHRONOUSLY VIA External Entity Data Item |
Formalization:
| External Entity Data Item.EE_ID | → | External Entity.EE_ID |
| R12. | External Entity CAN ASYNCHRONOUSLY COMMUNICATE VIA External Entity Event Data Item (1:Mc) |
| External Entity Event Data Item IS DATA FOR EVENTS OF External Entity |
Formalization:
| External Entity Event Data Item.EE_ID | → | External Entity.EE_ID |
| R13. | External Entity Event MAY CARRY External Entity Event Data Item (Mc:Mc) |
| External Entity Event Data Item IS CARRIED VIA External Entity Event | |
| External Entity Event Data ASSOCIATES External Entity Event AND External Entity Event Data Item 1-(Mc:Mc) |
Formalization:
| External Entity Event Data.EEevt_ID | → | External Entity Event.EEevt_ID | |
| External Entity Event Data.EE_ID | → | External Entity Event.EE_ID | |
| External Entity Event Data.EEedi_ID | → | External Entity Event Data Item.EEedi_ID | |
| External Entity Event Data.EE_ID | → | External Entity Event Data Item.EE_ID |
| R14. | Domain CONTAINS DEFINED Data Type (1:Mc) |
| Data Type DEFINES TYPES WITHIN Domain |
Formalization:
| Data Type.Dom_ID | → | Domain.Dom_ID |
| R15. | Data Type DEFINES THE TYPE OF External Entity Data Item (1:Mc) |
| External Entity Data Item IS DEFINED BY Data Type |
Formalization:
| External Entity Data Item.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID |
| R16. | Data Type DEFINES THE TYPE OF External Entity Event Data Item (1:Mc) |
| External Entity Event Data Item IS DEFINED BY Data Type |
Formalization:
| External Entity Event Data Item.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID |
| R17. | Data Type IS A (SUPERTYPE OF) Core Data Type |
| Data Type IS A (SUPERTYPE OF) User Data Type | |
Core Data Type IS A (SUBTYPE OF) Data Type | |
| User Data Type IS A (SUBTYPE OF) Data Type |
Formalization:
| Core Data Type.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID | |
| User Data Type.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID |
| R18. | Core Data Type DEFINES DOMAIN OF User Data Type (1:Mc) |
| User Data Type ARE DEFINED WITHIN Core Data Type |
Formalization:
| User Data Type.CDT_ID | → | Core Data Type.DT_ID |
| R19. | External Entity USES Bridge (1:Mc) |
| Bridge PROVIDES ACCESS TO External Entity |
Formalization:
| Bridge.EE_ID | → | External Entity.EE_ID |
| R20. | Data Type DEFINES THE RETURN VALUE Bridge (1:Mc) |
| Bridge RETURN VALUE DEFINED BY Data Type |
Formalization:
| Bridge.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID |
| R21. | Bridge IS PART OF Bridge Parameter (1:Mc) |
| Bridge Parameter CONTAINS Bridge |
Formalization:
| Bridge Parameter.Brg_ID | → | Bridge.Brg_ID |
| R22. | Data Type DEFINES THE TYPE OF Bridge Parameter (1:Mc) |
| Bridge Parameter IS DEFINED BY Data Type |
Formalization:
| Bridge Parameter.DT_ID | → | Data Type.DT_ID |